ARCH 655 Project 1_Case Study of Parametric Modeling,
Harbin Opera House, China
Hua Yan, MLA
Instructor: Dr. Wei Yan
Texas A&M University
Spring 2016
Introduction:
Architects: MAD Architects
Location: Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
Directors: Ma Yansong, Dang Qun, Yosuke Hayano
Area: 850000.0 ft2
Project Year: 2015
Photographs: Hufton+Crow, Adam Mørk
Harbin Opera House located in China, designed by MAD Architects in 2015. Some functions of Rhino-grasshopper, such as Kangaroo and weave-bird, are utilized to create parametric form (mass and skin) for modeling. The case study also includes alternative solution by physically-based modeling some analyses.
Objectives
The Case study aimed at using parametric modeling method to generate building model. The project of Harbin Opera House have three main parts, main building, annex building and outdoor plaza. I started for base foundation and used nurbcurve method to control the relationship between three parts.
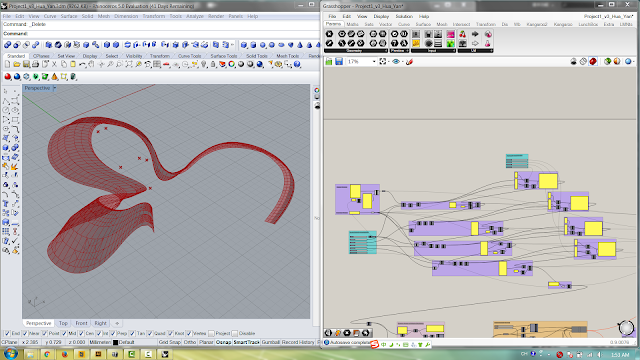
Base Structure Generation
Figure 1: Based on 13 given points, The base line was generated with nurbcurve method. Then, Functions of "Loft" and "Scale" help to create the curve surface and eventually finish the mass of building.
Figure 2: Variables for building mass.
Figure 3: Variables for outdoor plaza.
Kangaroo to create curved ceiling

Figure 4: In the line of top layer, several specific
points are selected for dome ceiling area by function icon of "cull
index". Then, using "Pline" function to Points to surface and using "weave bird" functions to convert surface to mesh.
The building ceiling with
wave form required more control points to control the shape of the ceiling.
Control points group 1: use "Naked Vertices", "Demesh" and "item" getting control points on the edges of mesh.
Control points group 2: first, bake points of function of "Naked Vertices", select suitable points to create form needed. second, manipulate clothed points: getting points coordinates with "cull index" and "panel" as 2nd group of points.
Figure 5 Result of ceiling by Kangaroo function.
Ceiling Structure Alternatives
Figure 6: Option 1_ Using edges of the mesh to create pipes and getting
structure.
Figure 7: Option 2 _Using points which were created by uv counts, and
then connecting adjacent points to generation pipe structure.
Glass Window Generation
Figure 8: Glass Window is generated by functions of "Diamond
grid" and "Weave"
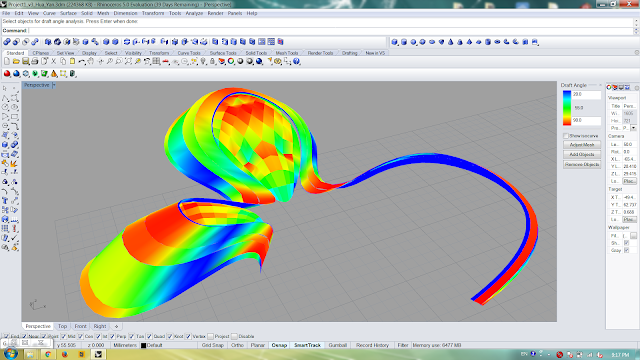
Analyses
Figure 9: Basic
Information analyses(color, length, area etc.)
Figure 10: Curvature analyses (grasshopper)
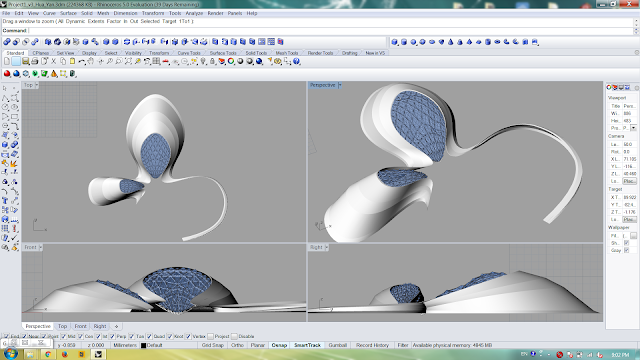
Plan and sections for the building model
Option 1
Option 2
All functions adopted in the parametric modeling
Model in rhino
Figure 12: Curvature analyses (Rhino)
Figure 13: Draft angle analyses (Rhino)
Figure 14: Environment map analyses (Rhino)
Figure 15: Zebra analyses (Rhino)
Rendering Effects
Reference:
Pallett, J., and Mark Burry. The new
mathematics of architecture. Thames and Hudson, 2010.
http://www.archdaily.com/778933/harbin-opera-house-mad-architects
http://www.i-mad.com/press/mad-architects-unveils-completed-harbin-opera-house/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DP975CpmuTA